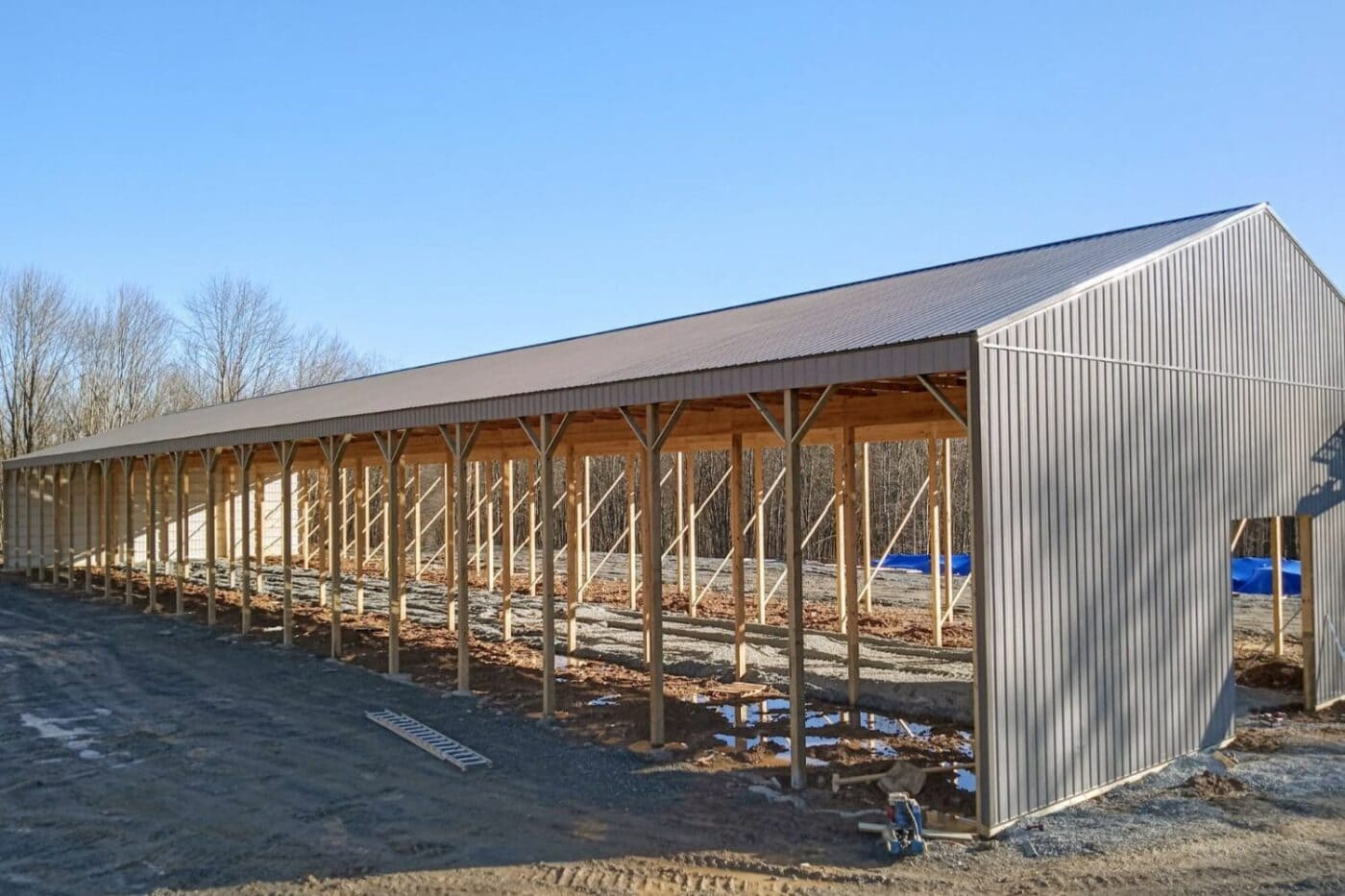
Introduction:
The construction industry has witnessed a significant shift towards metal buildings due to their durability, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. Among the crucial aspects of erecting a robust metal structure, framing stands out as a cornerstone in ensuring stability and longevity. This article delves into the intricacies of framing in metal building construction, exploring various methods, materials, and considerations that contribute to the success of such projects.
Understanding Metal Building Framing:
A. Structural Components:
- Main Frames: Exploring the primary load-bearing elements.
- Secondary Framing: The role of purlins, girts, and eave struts in distributing loads.
- Endwall Framing: Addressing the unique challenges posed by endwalls.
B. Types of Metal Building Systems:
- Clear Span Systems: Maximizing interior space without the need for interior columns.
- Modular Framing: Achieving flexibility and expansion capabilities.
- Single-Slope Systems: Adapting to specific architectural and functional requirements.
Materials and Techniques in Metal Building Framing:
A. Steel vs. Other Materials:
- Advantages of Steel Framing: Strength, durability, and environmental sustainability.
- Alternatives and Considerations: Comparing wood and other materials in framing.
B. Cold-Formed vs. Hot-Rolled Steel:
- Cold-Formed Steel: Ideal for smaller projects and intricate designs.
- Hot-Rolled Steel: Suitable for larger structures with heavier loads.
C. Framing Techniques:
- Welding vs. Bolted Connections: Weighing the pros and cons of each method.
- Pre-Engineered vs. Conventional Framing: Examining the benefits of pre-engineered systems.
Design Considerations and Challenges:
A. Load-Bearing Considerations:
- Wind and Seismic Loads: Addressing the impact of environmental factors.
- Snow Loads: Strategies for dealing with heavy snowfall in specific regions.
B. Thermal Bridging:
- Understanding the challenges of thermal bridging in metal framing.
- Thermal Break Solutions: Incorporating insulation and other techniques.
C. Expansion and Contraction:
- Designing for Thermal Movement: Preventing issues related to metal expansion and contraction.
- Expansion Joint Strategies: Ensuring structural integrity over time.
Case Studies and Best Practices:
A. Showcasing Successful Projects:
- Iconic Metal Buildings: Examining structures that have stood the test of time.
- Lessons Learned: Insights from real-world construction challenges and solutions.
B. Emerging Trends and Innovations:
- Technological Advancements: How digital tools are revolutionizing the design and construction of metal buildings.
- Sustainable Framing Practices: Incorporating eco-friendly materials and practices.
Conclusion:
Framing in metal building construction is a multifaceted process that requires a nuanced understanding of materials, techniques, and design considerations. As the construction industry continues to embrace the benefits of metal structures, mastering the art of framing becomes paramount for achieving resilient and sustainable buildings. This comprehensive guide aims to equip builders, architects, and industry professionals with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of metal building framing successfully.